Building an AI Agent to interact with Databases
May 2025 (1719 Words, 10 Minutes)
The following video shows that agent invoking a set of tools (functions) to answer the question provided
Contents
Introduction!
In this post, I’ll share my experience building an AI agent that can interact with databases, generate SQL queries, and provide data insights. This project uses LLMs and smolagents framework to create an ai agent to interact with databases.
The agent performs several key functions:
- Natural Language to SQL: Converts user questions in plain Language to SQL queries
- Query Execution: Safely executes the generated SQL queries against the database
- Data Analysis: Analyzes query results and generates meaningful insights
- Automatic Metadata Generation: Automicaly generat documenation on all database tables by looking at tables relationship and columns types and constraints and samples, this helps the agent understand the meaning and relationship between tables and possible usages
Agent Overview
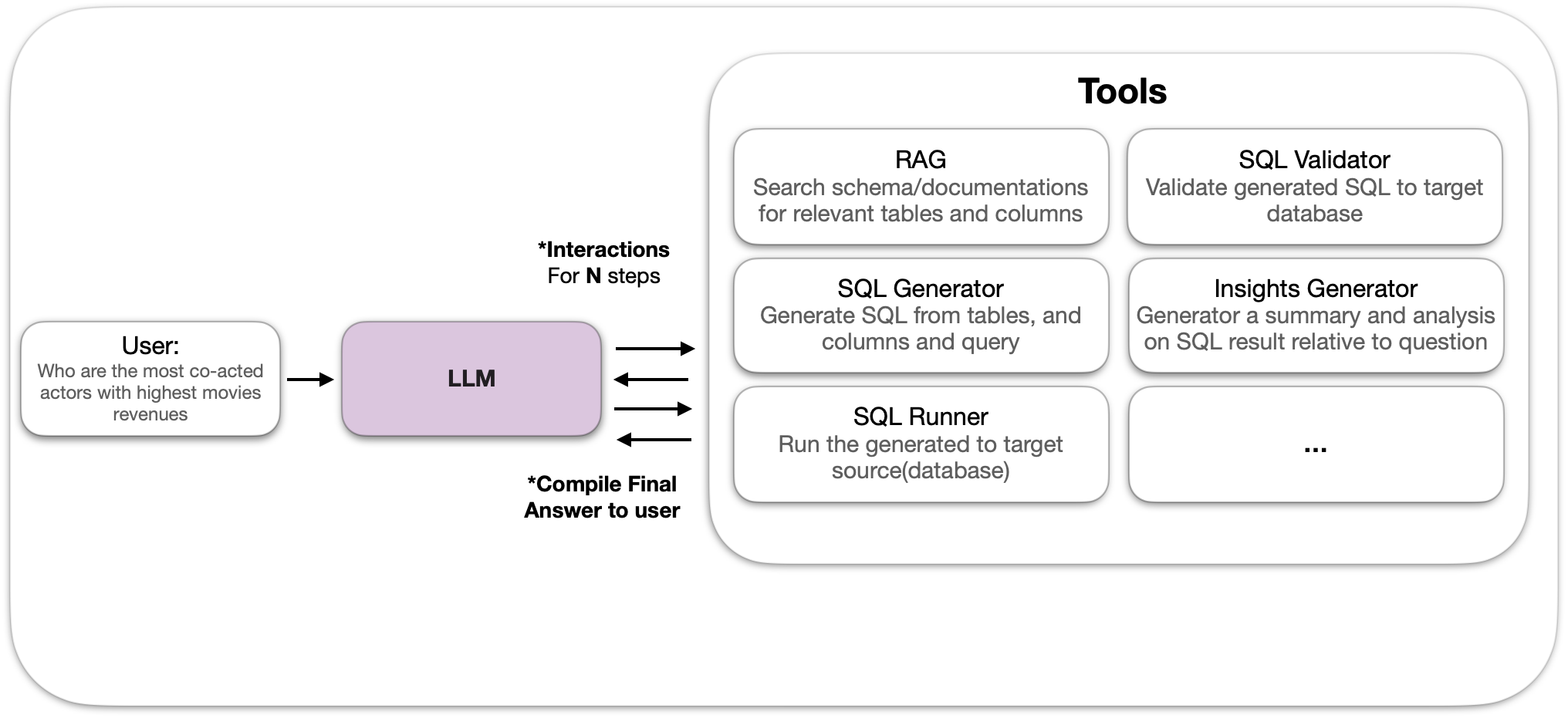
the agent runs in a loop analyzing and desciding which tools to invokes to answer the user question, untill it reaches max steps or it conclude it reached the answer the question
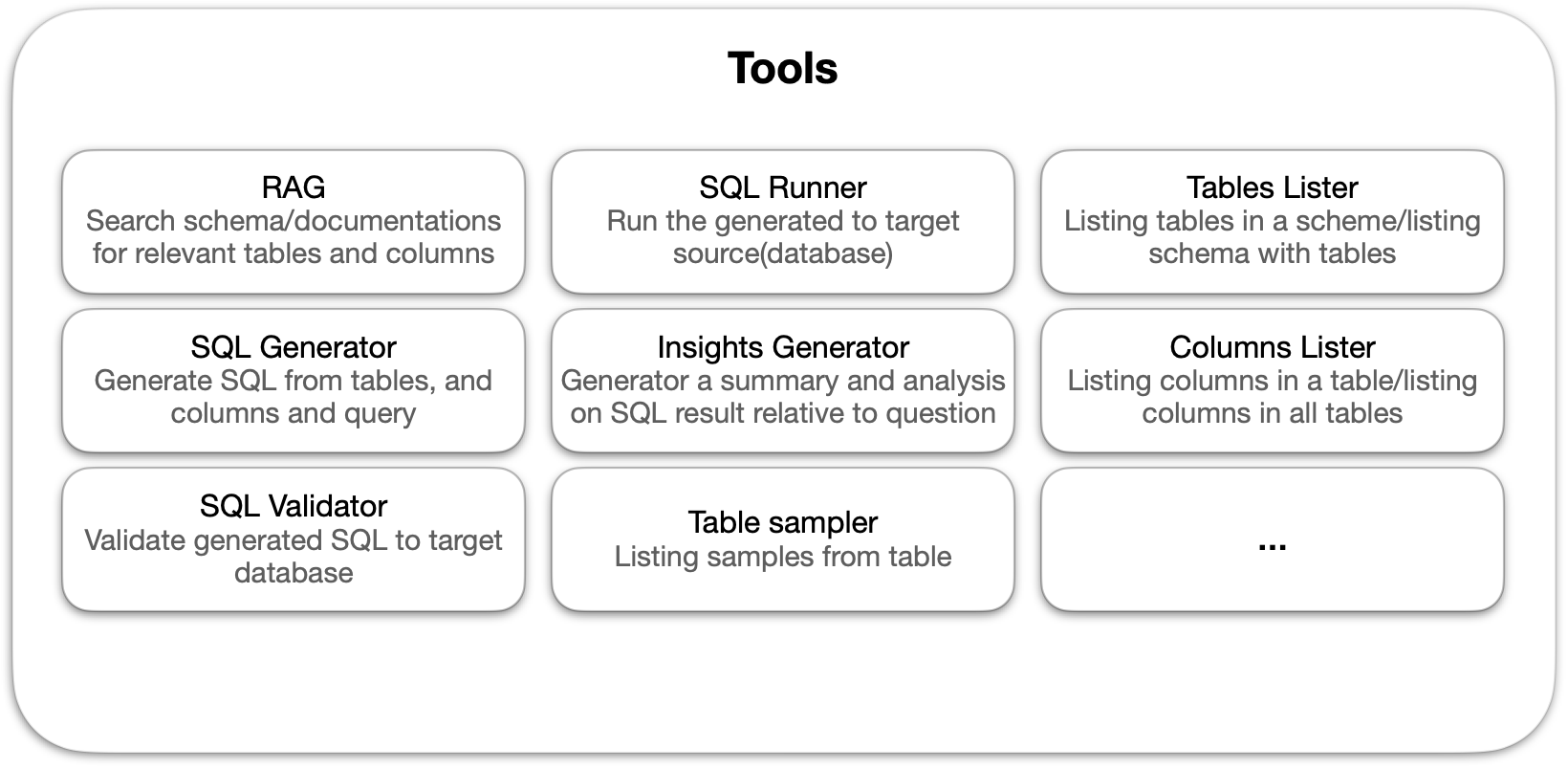
The agent has broader capablitiy to interact with databases and reach its goals. Below are tools with defintions.
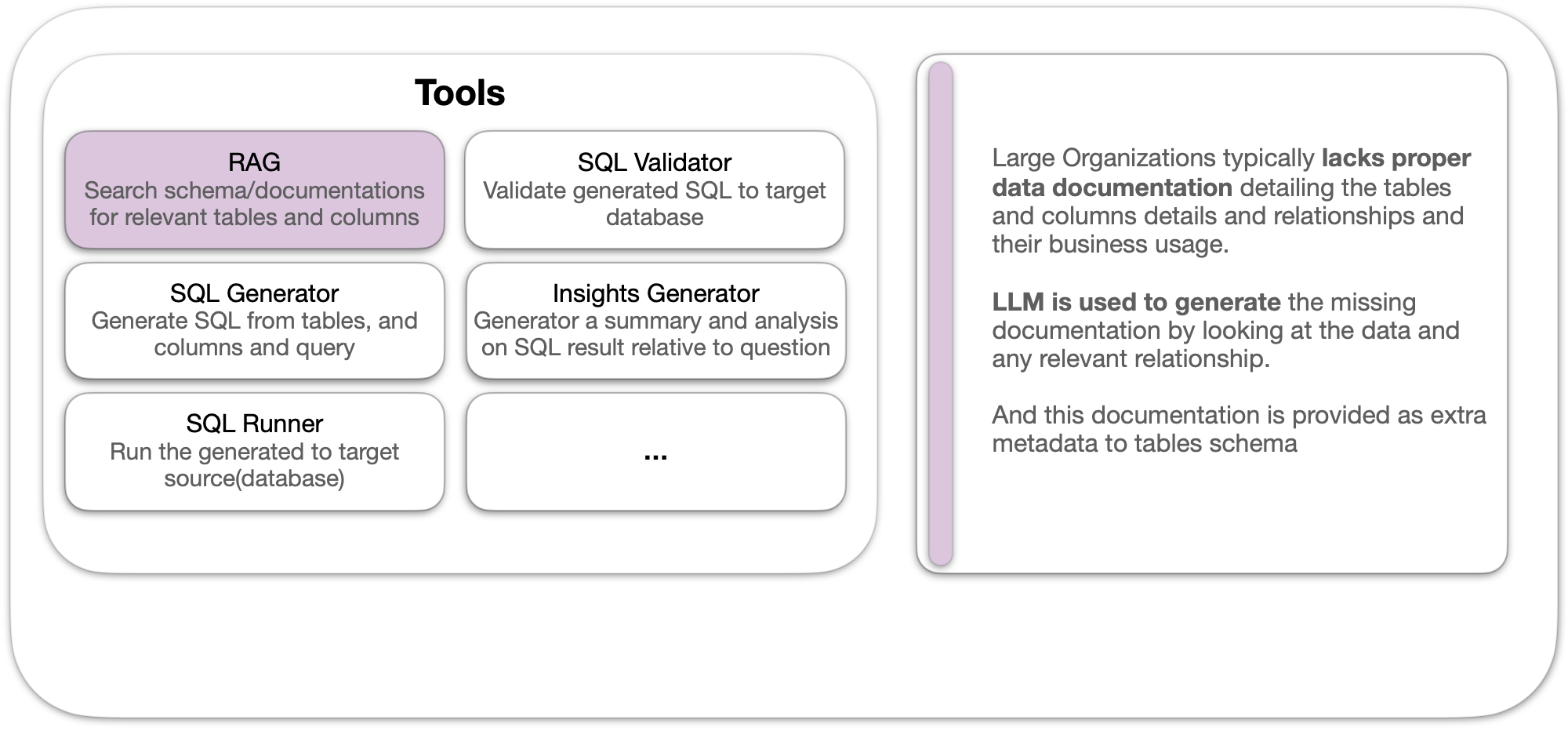
To ensure the agent has more context on the data it has instead of only passing schema we use an llm to generate documenation this happend when we connect a new source (database) we automatically generate metadata that is typically unavailable or outdated in large entrpsises, it aims to help the agent with more metadata on type of data it has access. And we generate them following this logic.
for each table we generate:
- Bussines summary: explaining the purpose and role of the table
- Possible usage scenarios for the table
for each column in this table we generate:
- Column summary: A detailed summary of what the column represents
- Bussines summary: explaining the significance of this data
- Possible usage scenarios for this column
- A list of relevant tags (e.g., identifier, text, timestamp, foreign key, etc.)
the following is the code to generate this documenation and evanutally stored into an interanl database with mapping to original columns and tables in source database
def _generate_documentation(
table_name: str, columns_data: List[dict], config: ChatCompletionConfig
) -> _TableDocumentation:
try:
# quick fix: for clickhouse do not have this type of infrommation, as it does not enforec foregins relationships
new_cols = []
for col in columns_data:
_col = {k: v for k, v in col.items() if k != "foreign_key_table_docs"}
if col.get("foreign_key_reference"):
_col["foreign_key_info"] = col.get("foreign_key_reference")
new_cols.append(_col)
except:
new_cols = columns_data
prompt = f"""
I need comprehensive documentation for a database table named '{table_name}' with the following columns:
{json.dumps(new_cols, indent=2)}
For each table, provide:
1. A business summary explaining the purpose and role of the table
2. Possible usage scenarios for the table
For each column, provide:
3. A detailed summary of what the column represents
4. A business summary explaining the significance of this data
5. Possible usage scenarios for this column
6. A list of relevant tags (e.g., identifier, text, timestamp, foreign key, etc.)
"""
messages = [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a data documentation expert.",
},
{"role": "user", "content": prompt},
]
try:
response = chat_completion_from_config(
messages, config, response_format=_TableDocumentation
)
return _TableDocumentation(**json.loads(response.choices[0].message.content))
except Exception as e:
raise e
This documenation powers the following tool that the agent can use to perform context search on any natural question and retireve extra metadata from the source tables and columns other than their schemas
class ContextRetrieverTool(Tool):
name = "context_retiver"
description = """this tool provides you similarity search on provided natural langague (question) against vector database to obtain most similar related tables and column names and their bussiness and usage documentation. and then joins the retireved
similar table names and columns and query the database to obatin its schema, as in datatypes, constraints. etc."""
inputs = {
"query": {
"type": "string",
"description": "a natural question to fetch most similar tables and columns with",
}
}
output_type = "string"
def forward(self, query: str):
return json.dumps(
get_context(
query=query, index=index, internal_db=internal_db, source=source_db
)
)
and to dynamically generate valid SQL compatible with source database used, we store database engine type at creation and pass them to SQL generator code dynamically this faciliate switchting from multiple engines with ease.
class DatabaseConfig(BaseModel):
engine: str = Field(description="The engine of the database")
class PostgresDatabaseConfig(DatabaseConfig):
user: str = Field(description="The user of the database")
password: str = Field(description="The password of the database")
host: str = Field(description="The host of the database")
port: int = Field(description="The port of the database")
dbname: str = Field(description="The name of the database")
schema_query_path: str = Field(description="The path to the schema query file")
class DuckDBDatabaseConfig(DatabaseConfig):
path: str = Field(description="The path to the DuckDB database file")
ddl_query_path: str = Field(description="The path to the ddl query file")
class ClickhouseDatabaseConfig(DatabaseConfig):
...
and this engine field is automaically passed to the agent tool to generate a valid sql
def generate_sql_from_context(query: str, context: List[dict], database : str, config: ChatCompletionConfig):
# quick fix for numpy array, should be fixed in the source
...
prompt = f"""
You are a SQL expert tasked with generating a SQL query based on a natural language question.
CONTEXT:
{context}
DATABASE: {database}
INSTRUCTIONS:
1. Generate a SQL query that answers the following question: "{query}"
2. Use only tables and columns that are mentioned in the CONTEXT section.
3. Make sure your query is syntactically correct and follows best practices for {database}.
4. Include appropriate JOINs when querying across multiple tables.
5. Add comments to explain your reasoning for complex parts of the query.
6. If the question cannot be answered with the available tables/columns, explain why.
Your response should be structured as follows:
SQL:
[Your SQL query here]
EXPLANATION:
[Your explanation of how the query works and any assumptions made]
RELEVANT SOURCES FROM CONTEXT:
[Your derived infromation from the context provided]
"""
...
The Agent and Custom Structured Output
the agent has two functionalities and each requries its own strcutred output response in both cases we override the default smolagents system prompt and customized it with more guidelines on how to return the final response. the two functions of the agents are:
- finder: the purpose is to act as assistant to data scientist [myself :)] as they’re interacting with databases and provide find whether information is present in database and what tables, columns, operation you need to run to extract it, think of instead of manually trying to find a specifc information it can look it up for you and return the SQL, tables, and columns without performing analysis just pure data expert. the response format for finder is
{
"sql":"sql query to answer the problem",
"tables":"list of tables from databases to answer the problem",
"columns":"list of columns from databases to answer the problem",
"operations":"list of operation to be done to answer the problem on tables and columns-NON-DATABASE default generic, like SELECT.",
"description":"The explanation of the query"
}
- query: it has more tools than finder and its purpose is to analyse the result and provide results of its SQL/s runs. and it has the following response format:
{
"analysis":"...",
"sql":"...",
"description":"The explanation of the query"
}
and to allow the agent to know which type of response to return we override the default system prompt and cusomtize the guideline on its final answer generation. the following snippet shows how it is done.
def create_agent(
task: str = "query",
engine=ENGINE,
planning_interval: int = 5,
additional_authorized_imports: list = DEFULAT_AUTH_IMPORTS,
tools: list = DEFAULT_TOOLS
):
if task == "query":
custom_prompt_templates = yaml.safe_load(
importlib.resources.files("core.prompts").joinpath("query_agent.yaml").read_text()
)
if task == "finder":
custom_prompt_templates = yaml.safe_load(
importlib.resources.files("core.prompts").joinpath("finder_agent.yaml").read_text()
)
agent = CodeAgent(
model=engine,
tools=tools,
additional_authorized_imports=additional_authorized_imports,
planning_interval=planning_interval,
prompt_templates=custom_prompt_templates,
)
return agent
Thank you for reading through, you can find the whole code below.